In today’s vaping landscape, the performance of e-liquid flavorings under thermal stress is no longer a niche concern — it is a fundamental quality metric. With high-powered mods, pod systems, and sub-ohm devices driving e-liquid temperatures beyond 200°C, the demand for heat-resistant flavoring compounds is growing rapidly. For both flavor developers and e-liquid manufacturers, understanding how to design and select thermal-resistant ingredients is now essential to ensure consumer satisfaction, regulatory compliance, and commercial success.
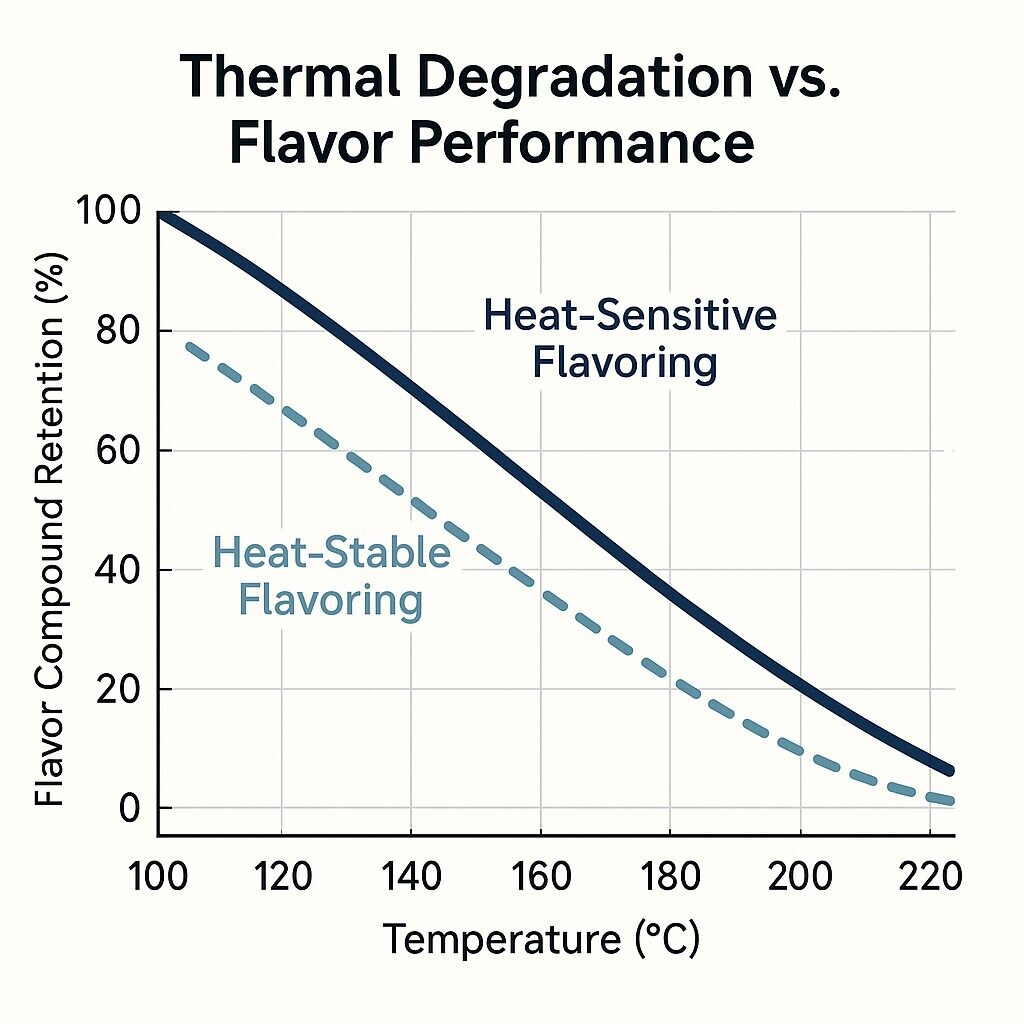
Thermal Degradation vs. Ejuice Flavorings Performance
Today’s vape devices, especially sub-ohm tanks and high-wattage mods, expose e-liquids to extreme thermal stress. This triggers a cascade of physical and chemical reactions in flavor compounds:
Implications:
Key Concern: Not all food-grade flavorings are designed to survive these thermal conditions.
Flavor compounds with boiling points below 180°C are especially vulnerable. At vape temperatures, they tend to evaporate rapidly or degrade. For instance:
Heavier molecules tend to resist vaporization. High molecular weight compounds, such as lactones, deliver robust base notes under high temperatures.
Practical Tip: Use flavor molecule analogs or protective matrices to anchor volatile compounds and reduce degradation.
Creating flavorings for high-temp e-liquids requires deliberate architectural thinking:
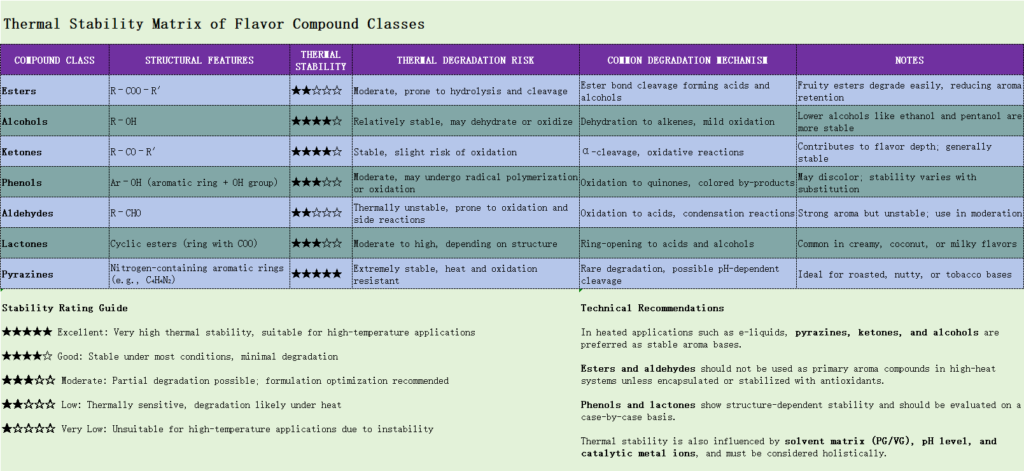
Thermal Survival Map of Common E-liquid Flavoring Classes
Flavor performance must be verified under simulated thermal stress. Recommended testing protocols:
Analyzes mass loss of flavoring samples across temperature gradients, identifying volatility points.
Quantifies breakdown compounds and identifies new byproducts.
Flavor panels assess aroma retention, clarity, and balance after exposure to 180°C–220°C for 10 seconds.
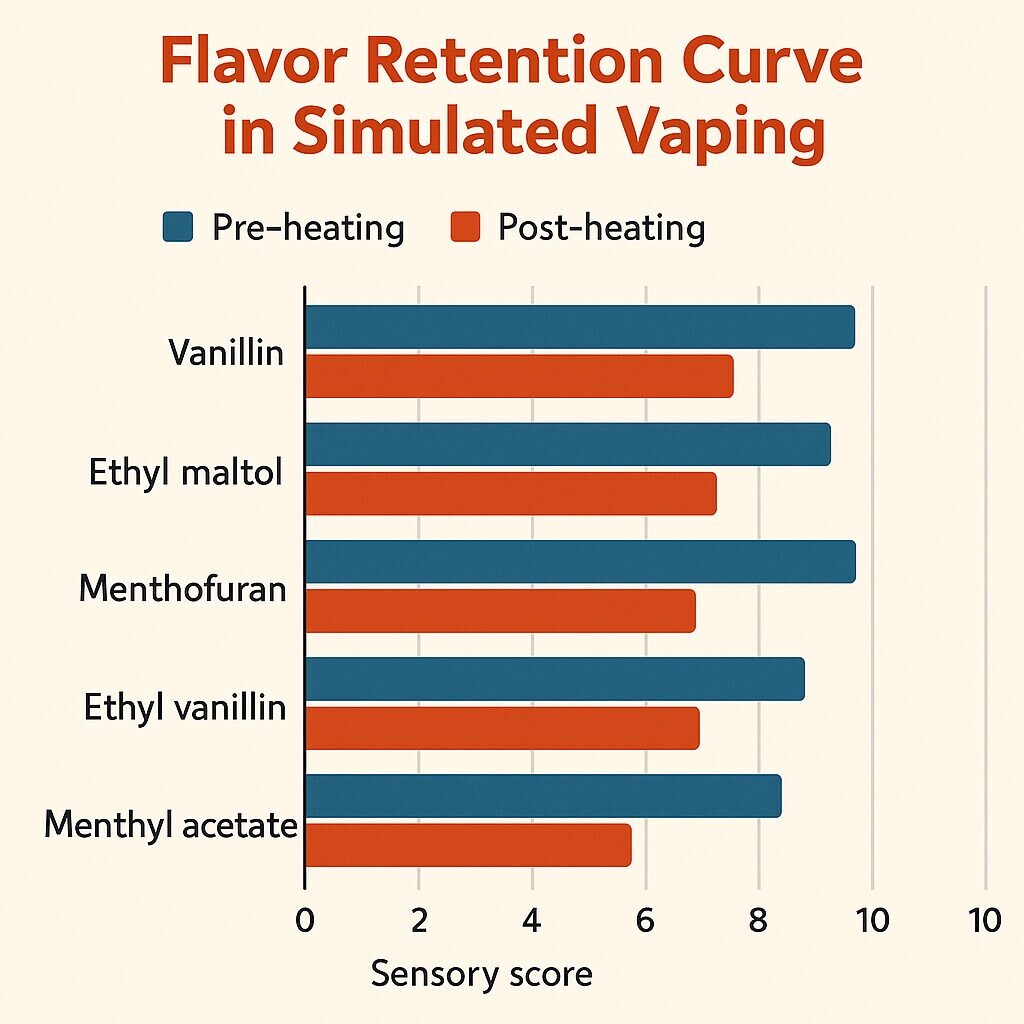
Flavor Retention Curve in Simulated Vaping
Carriers play a crucial role in flavor delivery and stability under heat.
Optimization Tip: Match carrier blend to the thermal sensitivity profile of the flavor compound matrix.
Creating heat-stable e-liquids is a multidisciplinary task. Success depends on partnerships with expert flavor developers. Key considerations:
Trusted Partner Tip: CUIGUAI Flavoring offers a specialized line of e-liquid flavorings engineered for high-temp stability, minimizing degradation while preserving full sensory richness.
Nano and microencapsulation protect volatile ingredients until vaporization, releasing flavor on-demand.
Designer aroma molecules crafted with thermal stability in mind, free of allergenic or unstable precursors.
Machine learning models that predict degradation pathways and optimize blends in silico.
Emerging Insight: Combining empirical lab data with predictive modeling reduces trial cycles and accelerates market-readiness.
As vaping devices evolve, thermal resilience is no longer optional — it’s a competitive differentiator. Only scientifically formulated, thoroughly tested flavorings will thrive in this environment.
Key Takeaways:

Formulation Checklist for Thermal-Resistant E-liquid Flavorings
Tags: heat-resistant flavoring, high-temp e-liquid, flavor stability vape, CUIGUAI Flavoring, vape formulation
Keywords: heat-resistant flavoring, high-temp e-liquid, flavor stability vape
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jun 3, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy