Keywords: microencapsulation vape flavor, controlled release aroma, e-liquid flavor retention, flavor stability vaping, CUIGUAI Flavoring
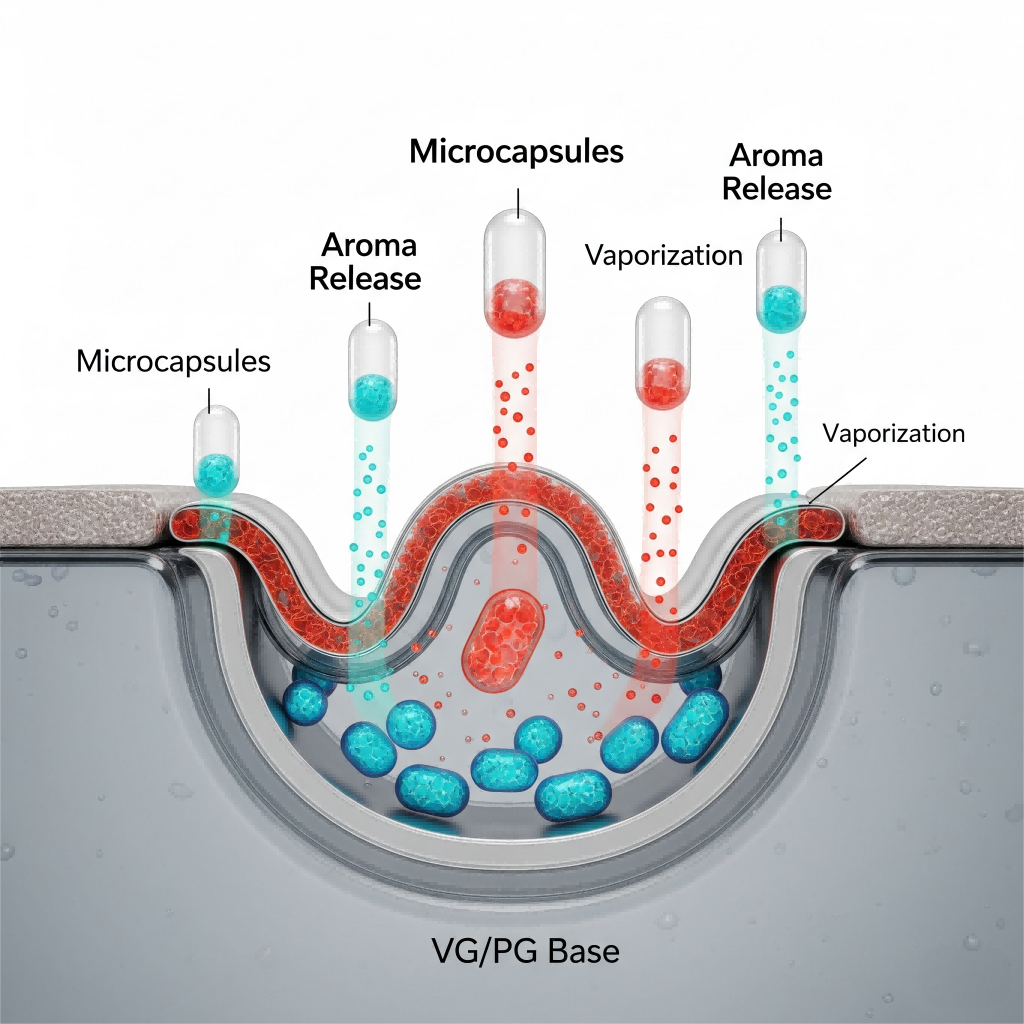
Cross-sectional diagram of microcapsules suspended in a VG/PG base
In the fast-evolving world of e-liquid development, flavor performance is not just a differentiator—it’s a survival factor. As consumer expectations rise for consistent, full-bodied taste across every puff and bottle, traditional flavor formulations are reaching their technical limits. Enter microencapsulation—a sophisticated method long applied in pharmaceuticals and functional foods—that is now revolutionizing e-liquid flavor delivery.
The promise? Precise, protected, and powerful aroma release. This technique offers formulators the ability to overcome oxidation, evaporation, and thermal degradation—delivering fresher, more authentic sensory experiences with every draw. This comprehensive guide will explore:
We’ll also introduce innovations from CUIGUAI Flavoring, a leader in encapsulated vape aroma systems.
Vape flavors are delicate by design. E-liquid flavor systems are typically composed of volatile, heat-sensitive compounds such as esters, aldehydes, ketones, and lactones. These molecules are prone to degradation at multiple stages:
The result: a phenomenon known as flavor drift, where the aroma profile shifts or diminishes with time or device use. For high-end e-liquids, this inconsistency is unacceptable.
Microencapsulation involves enclosing active substances—in this case, flavor compounds—within protective shell materials to form microcapsules ranging from 1 to 500 microns. This enables controlled release, stability enhancement, and targeted delivery.
Shell materials can include polysaccharides (gum arabic, maltodextrin), lipids (lecithin, waxes), or synthetic polymers (ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol), chosen based on the intended release mechanism.
A range of encapsulation techniques are suitable for e-liquid applications, depending on cost, compound volatility, and device interaction.
One of the most scalable and affordable techniques, spray drying involves atomizing a flavor emulsion into hot air, rapidly solidifying the outer wall.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Cases:
This technique uses electrostatic interaction between two polymers to form a gel-like capsule wall around a flavor core.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Cases:
Liposomes are vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that encapsulate hydrophobic or hydrophilic flavors.
Pros:
Cons:
Use Cases:
Cyclodextrins are cyclic oligosaccharides that trap small hydrophobic molecules within their hydrophobic core.
Pros:
Cons:
• Some may impact viscosity in PG/VG blends
Use Cases:
Encapsulation Method Comparison Matrix for E-liquid Formulators
Traditional e-liquids release all volatile compounds immediately upon heating, leading to rapid sensory fatigue and diminishing returns on complex blends.
This allows developers to engineer flavor progression such as:
These sensory sequences significantly enhance flavor richness and retention, aligning vaping more closely with multi-phase gustatory experiences found in fine foods or wines.
CUIGUAI Flavoring is among the first China-based flavor manufacturers to commercially deploy microencapsulation in vape-specific aromas.
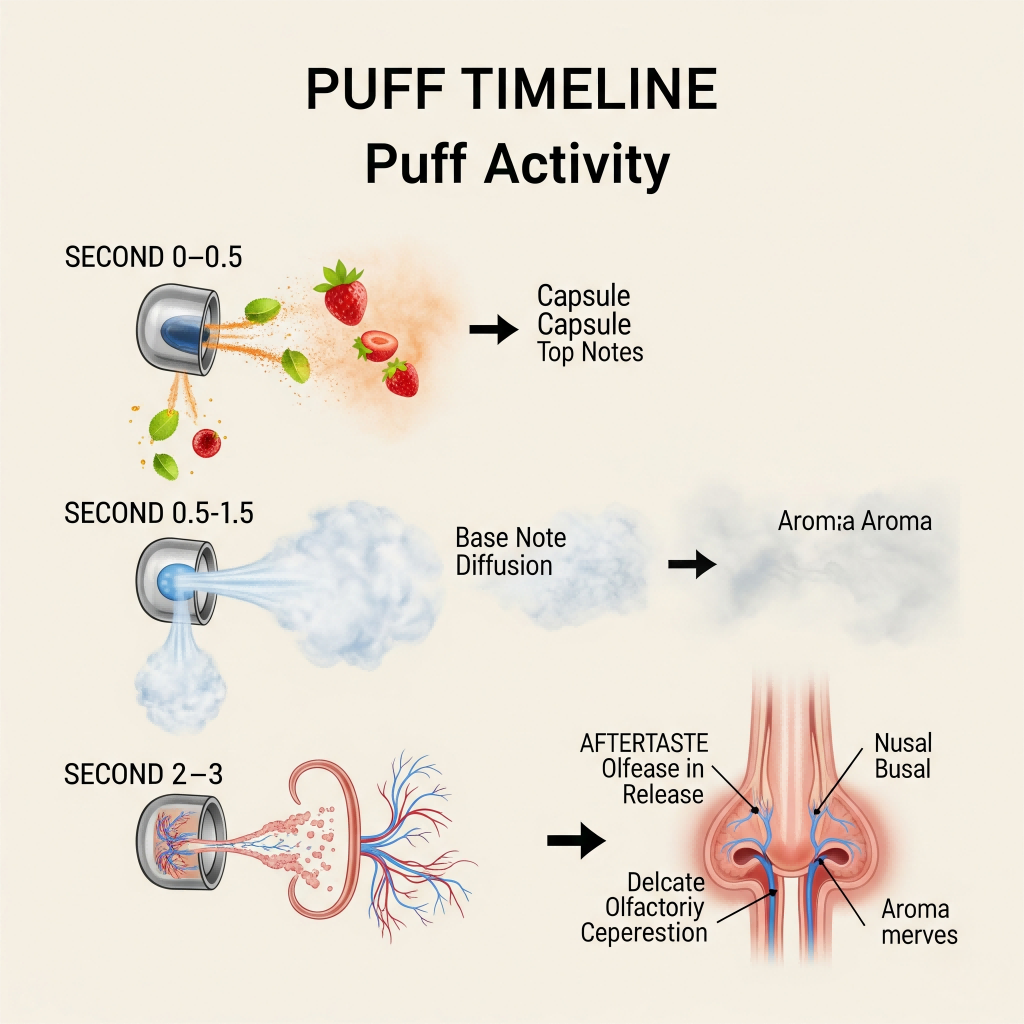
Timeline showing 0-3 seconds of puff activity
Microencapsulation isn’t plug-and-play—it requires precision. Here are common challenges and CUIGUAI’s methods to address them:
Some encapsulants are unstable in PG/VG. CUIGUAI uses solvent-resistant shell polymers tested in 70/30 and 50/50 ratios.
Poorly engineered capsules may clog or underperform. CUIGUAI’s capsules are thermally profiled via TGA (Thermogravimetric Analysis) to ensure full release within typical vaping ranges.
Heat curve differences between mesh and wire coils can impact release. CUIGUAI tailors encapsulation parameters for:
E-liquid flavor encapsulation must meet food and inhalation safety standards. CUIGUAI’s encapsulation protocols comply with:
CUIGUAI also provides batch-specific technical documentation for OEM and export clients.
CUIGUAI’s next-gen development platform integrates:
These future-forward systems may soon allow:
Vape Flavor Innovation Roadmap (2025–2030)
As consumer demands for quality, consistency, and sensory complexity grow, microencapsulation becomes a critical differentiator for brands. It ensures:
With CUIGUAI Flavoring leading the innovation frontier, vape brands now have access to encapsulated aroma systems that deliver stability, performance, and competitive edge.
Want to transform your vape product line with advanced flavor engineering?
Contact CUIGUAI Flavoring today for:
CUIGUAI Flavoring – Where Flavor Science Meets Vaping Innovation.
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Jul 03, 2025
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy