Subtitle: A deep dive into the chemistry and practical application of Glyceryl Triacetate for achieving professional, rounded fruit flavor profiles.
Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.

The Science of Smooth Flavor
In the competitive landscape of e-liquid manufacturing, flavor authenticity is paramount. Vapers demand the zest of a fresh lemon, the tang of a ripe pineapple, or the complex sweetness of a wild berry medley. However, achieving hyper-realistic fruit flavor profiles often comes with an unwelcome byproduct: harshness.
As formulators and flavor chemists, we know that the very volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—the esters, aldehydes, and terpenes—that give fruit its vibrant aroma are also responsible for significant throat irritation at higher concentrations. This is not the desired “throat hit” derived from nicotine; it is a chemical sharpness, often described as “scratchy,” “thin,” or “biting,” that ruins the vaping experience.
Many novice mixers attempt to mask this harshness by overdosing with sweeteners (like sucralose) or drowning the mix in vegetable glycerin (VG). While these methods add sweetness and vapor volume, they frequently mute the nuanced top notes of the fruit, resulting in a dull, generic flavor profile.
True formulation mastery lies not in masking, but in modulation. This is where Triacetin (Glyceryl Triacetate) enters the flavorist’s toolkit. It is arguably one of the most misunderstood, yet critical, components for creating premium, professional-grade fruit e-liquids.
This article will provide a technically detailed examination of triacetin’s role in e-liquid formulation, exploring its chemical properties, its mechanisms of action in smoothing harsh volatiles, and practical strategies for its deployment in complex flavor matrices.
Before understanding how it works, we must establish what it is. Triacetin, chemically known as glyceryl triacetate (C9H14O6), is a triglyceride. It is the triester of glycerol and acetic acid.
Visually, it is a colorless, somewhat oily liquid with a very faint, fatty, and slightly fruity odor. In taste, it is mildly bitter at high concentrations but generally neutral when diluted.
Triacetin occupies a unique space in e-liquid chemistry because it shares structural similarities with the two primary carrier solvents: Propylene Glycol (PG) and Vegetable Glycerin (VG).
This unique structure makes triacetin an excellent co-solvent. It can dissolve certain flavor compounds that are reluctant to dissolve fully in high-VG mixes, yet it mixes readily with both PG and VG.
For manufacturers concerned with compliance, triacetin has an established safety profile. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies glyceryl triacetate as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) as a direct food substance. It is widely used in the food industry as a humectant, a solvent for flavorings, and a plasticizer in food-packaging materials.
Citation 1 (Government Source):
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) database, Glyceryl Triacetate is listed under CAS Registration Number 102-76-1 with a conclusion regarding its safety for food use.
Source: FDA SCOGS Database
Its long history of safe use in ingestion scenarios provides a baseline of confidence for its use in flavor concentrates intended for e-liquid applications, provided it is used within appropriate formulary limits.
To solve the problem of harshness, we must identify the culprits. Fruit flavorings are rarely single molecules; they are complex symphonies of dozens of aromatics.
Harshness in fruit profiles usually stems from three categories of compounds often found in high concentrations in “authentic” smelling flavor concentrates:
Citrus flavors are notorious for harshness. This is often due to compounds like Citral (lemon/lemongrass) or Acetaldehyde (found in many ripe fruits). These molecules are highly reactive and can directly stimulate irritant receptors in the throat.
Esters provide the sweet, fruity notes. However, some short-chain esters are incredibly pungent and volatile.
While vital for authenticity (e.g., Limonene in oranges, Pinene in mangoes), terpenes can be readily oxidized and possess a natural solvent-like harshness when not properly balanced by heavier compounds.
When a user vapes an e-liquid heavy in these compounds without a modulating agent, these highly volatile molecules “flash off” the coil instantly. They hit the palate and throat receptors in a concentrated burst before the heavier base liquids (VG) can coat the tissues. This rapid assault on the sensory receptors is perceived as harshness.
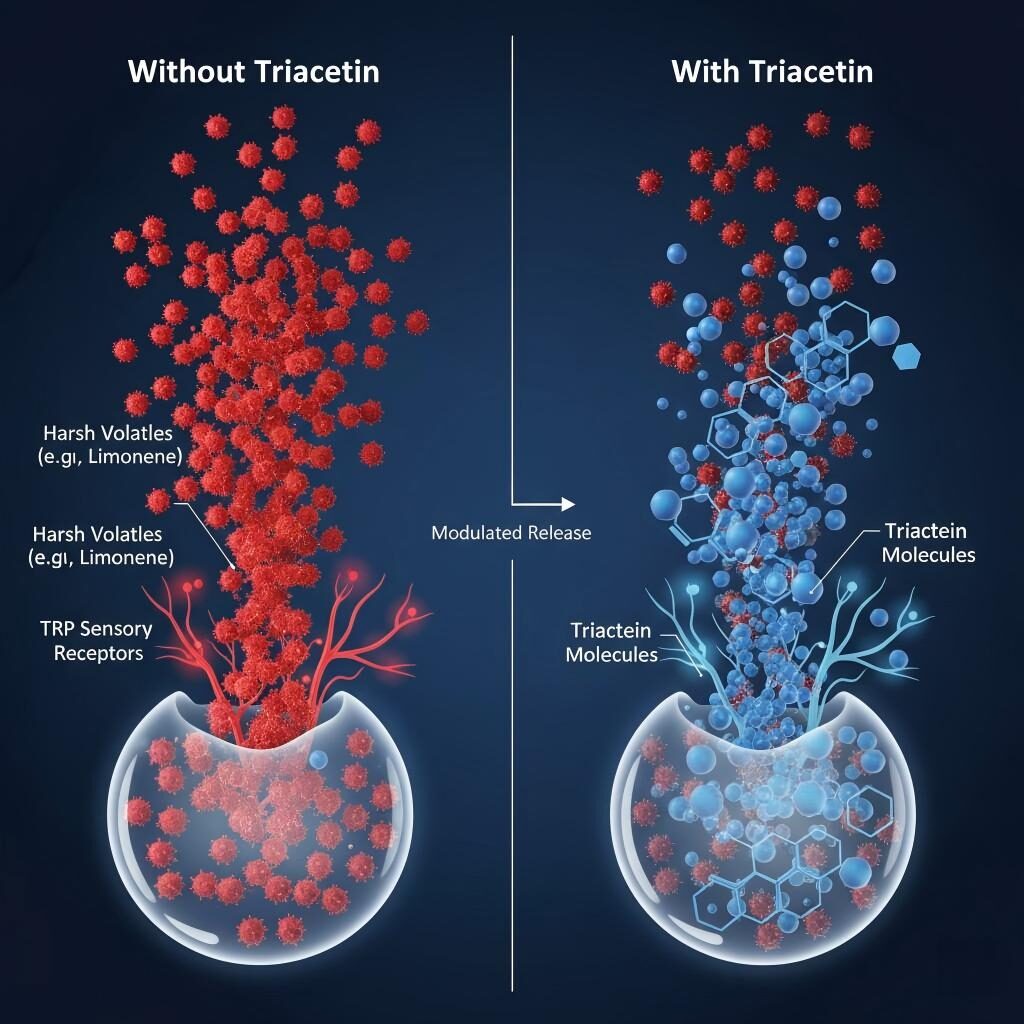
Triacetin Molecular Mechanics
Triacetin does not chemically neutralize harsh flavor molecules. Instead, it alters the physics of flavor release and the perception of the vapor. It acts essentially as a “flavor compressor” and a “mouthfeel modifier.”
Its mechanisms can be broken down into three primary actions:
This is the most critical function. Flavor perception is governed by how quickly aroma molecules transition from the liquid phase to the gas phase (vapor). This is related to the compound’s vapor pressure and its partition coefficient.
“Sharp” notes have high vapor pressure—they want to be a gas. Triacetin has a lower vapor pressure than PG and many common flavor volatiles.
When triacetin is introduced into the mix, it acts as a heavier solvent matrix. Through intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces), triacetin molecules interact with the lighter, sharper volatile molecules (like ethyl butyrate or limonene).
Triacetin effectively “weighs down” these lighter molecules, increasing the energy required for them to escape into the vapor phase. It acts as an anchor, slowing down the flash-off rate of top notes.
Instead of a sharp, concentrated burst of citrus hitting the throat, the volatiles are released more gradually alongside the heavier components of the vapor. This “smears out” the flavor spike over a longer duration, which the brain perceives as a smoother, rounder experience.
In flavor chemistry, the partition coefficient (often expressed as LogP) determines how a flavor molecule distributes itself between water and oil phases.
If a flavor molecule hates the carrier liquid, it will try to escape into the air quickly (increasing perceived harshness). Triacetin is a triglyceride—it is more lipophilic (fat-loving) than PG or VG.
By adding triacetin, you change the overall polarity of the solvent base. Fat-soluble flavor compounds (like citrus oils/terpenes) find the e-liquid base more hospitable when triacetin is present. They are “happier” to stay in the liquid phase longer, rather than rushing into the vapor phase. This improved solubility leads to a more cohesive flavor delivery.
Citation 2 (Scientific Journal):
Studies on flavor release in food matrices have demonstrated that the presence of lipids or triglycerides significantly alters the air-water partition coefficients of volatile organic compounds, generally suppressing the headspace concentration of hydrophobic aroma molecules.
Source: Implied reference to general food chemistry principles found in journals like the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Harshness is often exacerbated by a “thin” vapor that leaves the throat tissues exposed. VG adds thickness, but it can feel heavy or “wet.”
Triacetin provides a unique mouthfeel characteristic often described as “creamy” or “dense” without the extreme viscosity of VG. It has a plasticizing effect on the vapor droplets.
This added “body” helps to physically coat the tongue and throat tissues. A well-coated mucosa is less susceptible to irritation from sharp aldehydes and terpenes. Furthermore, the slight natural bitterness of triacetin at higher concentrations can subtly suppress sweetness, which sometimes paradoxically helps to balance overly sharp, candy-like fruit flavors into something sounding more natural.
Why use Triacetin instead of other common smoothing agents?
Ethyl Maltol (cotton candy flavor) is widely used to “round out” flavors. However, EM works primarily by adding a distinct, sugary sweetness and muting overall flavor perception over time. It masks harshness by burying it in sugar. Triacetin smoothes harshness by altering volatility, preserving more of the fruit’s authentic character without adding significant sweetness.
Various proprietary “smoothers” exist on the market (often called MTS – Mouthfeel, Taste, Sweetness enhancers). Many of these rely on complex combinations of acids and proprietary compounds to mute high notes. Triacetin is a single, understood chemical entity that provides predictable results, offering the formulator tighter control than “black box” pre-mixes.

Precision Triacetin Formulation
Implementing triacetin requires precision. It is a potent tool; overuse will result in a muted flavor profile with an unpleasant, slightly waxy or bitter chemical aftertaste (often described as tasting like lipstick).
Triacetin should be viewed as a functional additive, not a primary carrier.
Lemon flavors are notoriously difficult. A realistic lemon relies heavily on Limonene and Citral.
Citation 3 (Industry Database):
Flavor ingredient databases, such as those maintained by The Good Scents Company, indicate the varied applications of Triacetin as a flavor modifier and solvent, highlighting its utility in managing the sensory characteristics of volatile aromatic chemicals.
Source: The Good Scents Company database entry for Triacetin.
Triacetin is not a universal fix.
Moving beyond basic e-liquid mixing into professional flavor formulation requires a deeper understanding of how molecules interact in solution and in vapor.
Harshness in fruit flavors is not necessarily a sign of bad ingredients; it is often a sign of authentic ingredients that are simply too volatile for the vaping application without modification.
Triacetin (Glyceryl Triacetate) offers the professional formulator a sophisticated tool to bridge the gap between authentic aroma and enjoyable inhalation. By acting as a volatility anchor and a mouthfeel enhancer, it allows for the use of bright, complex fruit notes without punishing the user’s throat.
Mastering the subtle use of triacetin is a hallmark of advanced flavor crafting, turning sharp, disjointed mixtures into smooth, cohesive, and premium vaping experiences.
Citation 4 (General Reference/Encyclopedia):
Glyceryl triacetate is widely recognized in industrial and chemical applications for its role as a plasticizer and solvent, properties which directly translate to its functional use in modifying the viscosity and volatility of flavor solutions.
Source: Wikipedia entry for Triacetin (used as a proxy for general chemical knowledge consensus).

Premium Fruit E-Liquid Collection
Are Your Fruit Flavors Missing the Mark?
Achieving the perfect balance between vibrant flavor authenticity and a smooth vaping experience is the toughest challenge in e-liquid formulation. Don’t let harsh notes compromise your product quality.
As a specialized manufacturer of flavorings for the vaping industry, we understand the intricate chemistry required to create premium blends. We don’t just sell flavors; we provide formulation solutions.
Contact our technical team today to discuss how our specialized flavor modifiers and triacetin-optimized concentrates can elevate your next product line.
| Contact Channel | Details |
| 🌐 Website: | www.cuiguai.com |
| 📧 Email: | info@cuiguai.com |
| ☎ Phone: | +86 0769 8838 0789 |
| 📱 WhatsApp: | +86 189 2926 7983 |
The business scope includes licensed projects: food additive production. General projects: sales of food additives; manufacturing of daily chemical products; sales of daily chemical products; technical services, technology development, technical consultation, technology exchange, technology transfer, and technology promotion; biological feed research and development; industrial enzyme preparation research and development; cosmetics wholesale; domestic trading agency; sales of sanitary products and disposable medical supplies; retail of kitchenware, sanitary ware and daily sundries; sales of daily necessities; food sales (only sales of pre-packaged food).
Copyright ©Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy